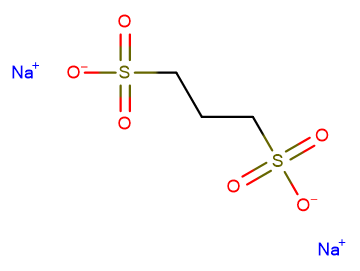
Eprodisate disodium
CAS No. 36589-58-9
Eprodisate disodium( Eprodisate Disodium | Eprodisate sodium | Kiacta )
Catalog No. M14258 CAS No. 36589-58-9
Eprodisate Disodium is the orally available disodium salt form of Eprodisate, a negatively charged sulfonated inhibitor of fibrillogenesis, that can be used in the treatment of amyloid A (AA) amyloidosis.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 30 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 42 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 61 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameEprodisate disodium
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionEprodisate Disodium is the orally available disodium salt form of Eprodisate, a negatively charged sulfonated inhibitor of fibrillogenesis, that can be used in the treatment of amyloid A (AA) amyloidosis.
-
DescriptionEprodisate Disodium is the orally available disodium salt form of Eprodisate, a negatively charged sulfonated inhibitor of fibrillogenesis, that can be used in the treatment of amyloid A (AA) amyloidosis.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsEprodisate Disodium | Eprodisate sodium | Kiacta
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorSAA
-
Research AreaOther Indications
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number36589-58-9
-
Formula Weight248.19
-
Molecular FormulaC3H6Na2O6S2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilitySoluble in Water
-
SMILESO=S(CCCS(=O)([O-])=O)([O-])=O.[Na+].[Na+]
-
Chemical Name1,3-Propanedisulfonic acid, disodium salt
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Bayes M, et al. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2007 Apr;29(3):231-45.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Ethyl Vanillate
Ethylvanillin are used by the food industry; ethylvanillin is more expensive, but has a stronger note.
-
3beta-Androstanediol
3beta-Androstanediol is an endogenous estrogen.?
-
Nudiposide
Nudiposide has significant neuroprotective activities against glutamate-injured neurotoxicity in HT22 cells.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


